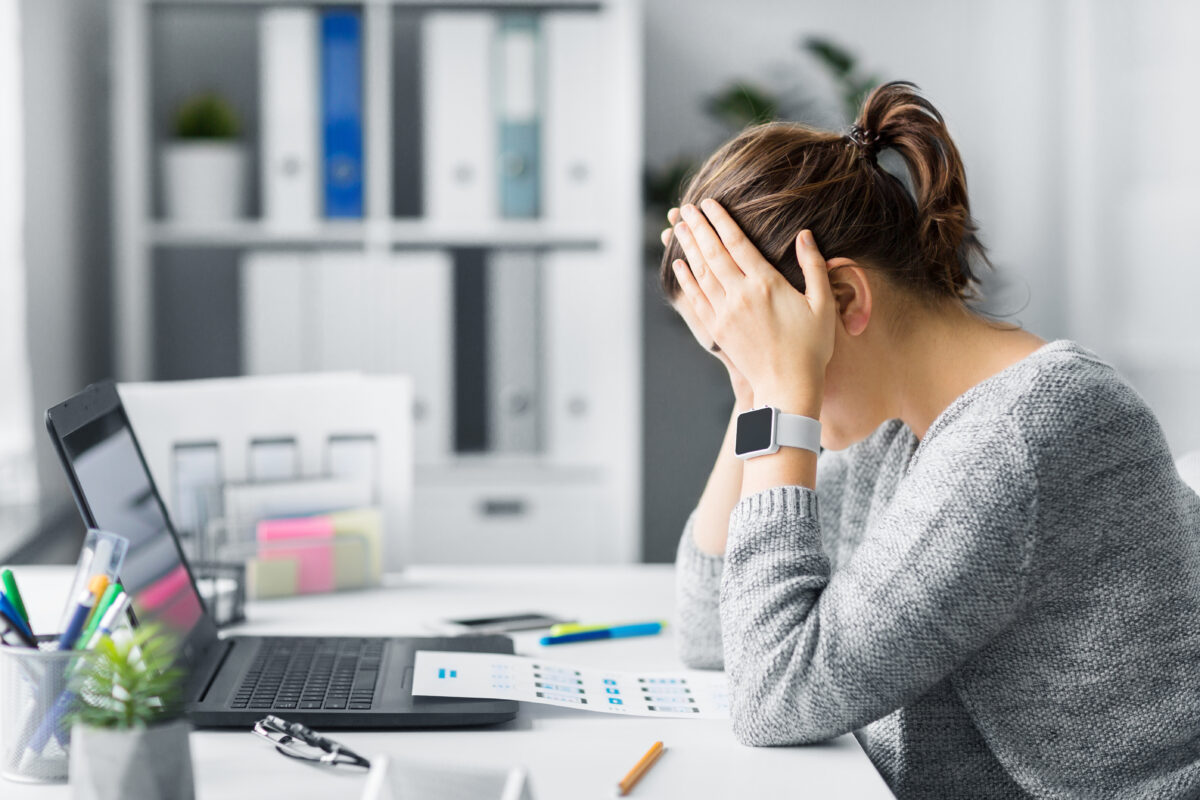
In our recent blog post – “Body Composition” is the new “Weight Loss” we referred to stress and the impact it has on your Metabolism by disrupting hormone levels and it’s always bad.
In 21st century life can be very difficult if not impossible to not experience any stress but that doesn’t mean we should accept it as a fact of life.
Firstly, don’t throw a blanket over the word “Stress”, all stress is not equal. Type, Term and Impact are important factors, and they vary.
Here are the main types of stress:
- Acute stress: This type of stress is short-term and is a normal response to a specific situation, such as public speaking or meeting a tight deadline.
- Chronic stress: This type of stress is long-term and can have negative impacts on physical and mental health. Chronic stress can result from ongoing life stressors, such as financial difficulties, relationship problems, or a high-stress job.
- Psychological stress: This type of stress is related to mental or emotional demands, such as relationship conflicts, work-related stress, or loss of a loved one.
- Physiological stress: This type of stress is related to physical demands, such as injury, illness, or exposure to extreme temperatures.
- Traumatic stress: This type of stress is related to a traumatic event, such as a natural disaster, physical assault, or a serious accident.
- Environmental stress: This type of stress is related to environmental factors, such as noise pollution, overcrowding, or exposure to toxins.
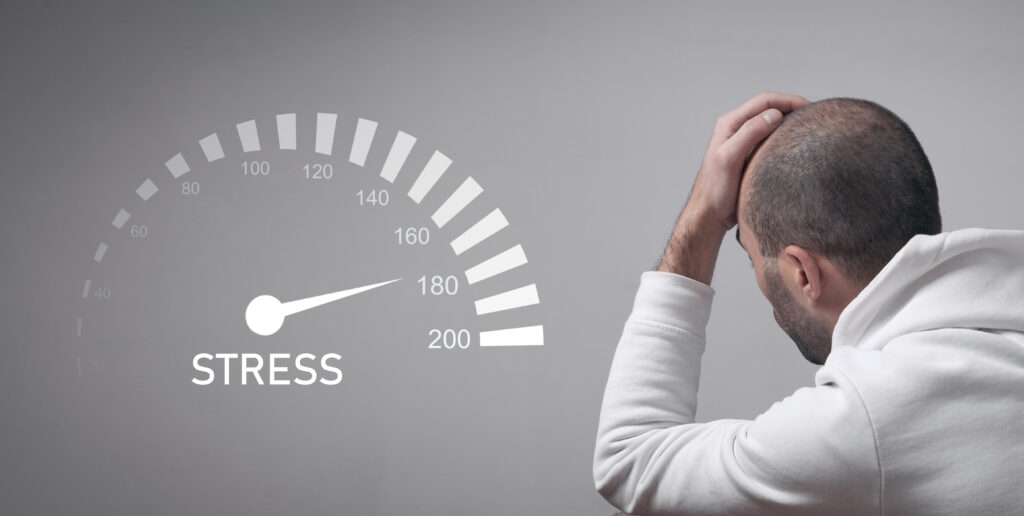

Some of the above are chronic or long-term and can have a negative impact on your physical and mental health. Make sure you consult your Doctor and mental health professional in isolating these stress types.
Don’t get used to having stress and accepting it. Recognize it and remember to be mindful that being stressed affects the people around you as well.
Here are some symptoms you should that are common indicators:
- Physical symptoms: headaches, muscle tension or pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, digestive problems, and changes in appetite.
- Emotional symptoms: anxiety, depression, irritability, mood swings, feelings of overwhelm, and difficulty concentrating.
- Behavioral symptoms: changes in eating habits, increased alcohol or drug use, and decreased physical activity.
- Cognitive symptoms: forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, and indecisiveness.
It is important to manage your stress by finding ways to manage it including:
- Exercise
- Mindfulness
- Relaxation techniques
- Self-care
- Environment control

Here are several practical steps you can take to reduce your overall stress levels, including:
- Exercise regularly: Exercise has been shown to reduce stress and improve mental health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity most days of the week.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep is essential for regulating hormones and reducing stress. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support overall health and reduce stress.
- Connect with others: Spending time with friends and family and participating in social activities can help reduce stress and improve mood.
- Manage your time effectively: Time management can help reduce stress by ensuring that you have enough time for important tasks and activities.
- Take breaks and prioritize self-care: Taking regular breaks and engaging in self-care activities, such as getting a massage or taking a relaxing bath, can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.

It’s important to find the stress-management strategies that work best for you and to make them a regular part of your daily and life’s routine. Consulting with a healthcare professional is always a good idea if you have concerns about your stress levels.